Sumador completo
Sumador Completo
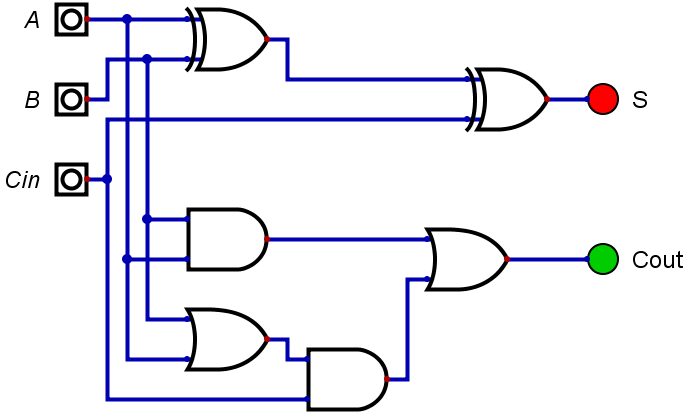
El sumador completo supone un circuito un poco más complejo. A diferencia del semisumador, nos permite incluir en la suma de dos bits el acarreo de una suma anterior a través de una entrada que se llama Cin, con lo que ya podremos realizar cualesquiera sumas.
Según lo dicho, tendremos tres variables de entrada, a las que llamaremos A, B y la propia Cin y dos de salida: s, la suma y Cout, el acarreo de la misma (si procede). Entonces, la tabla de verdad quedará:
| A | B | Cin | S | Cout |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Una vez simplificadas las funciones e implementadas, se obtiene el siguiente circuito:
library IEEE;
use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL;
-- Uncomment the following library declaration if using
-- arithmetic functions with Signed or Unsigned values
--use IEEE.NUMERIC_STD.ALL;
-- Uncomment the following library declaration if instantiating
-- any Xilinx primitives in this code.
--library UNISIM;
--use UNISIM.VComponents.all;
entity sumadorcompleto is
Port ( a : in STD_LOGIC;
b : in STD_LOGIC;
cin :
in STD_LOGIC;
s1 :
out STD_LOGIC;
cout :
out STD_LOGIC);
end sumadorcompleto;
architecture Behavioral of sumadorcompleto is
component compuertand2 is
Port ( a : in STD_LOGIC;
b : in STD_LOGIC;
q :
out STD_LOGIC);
end component;
component compuertaxor is
Port ( a : in STD_LOGIC;
b : in STD_LOGIC;
q :
out STD_LOGIC);
end component;
component compuertaor2 is
Port ( a : in STD_LOGIC;
b : in STD_LOGIC;
q :
out STD_LOGIC);
end component;
signal c1, c2, c3, c4 : std_logic;
begin
U0: compuertaxor PORT MAP (a,b,c1);
U1: compuertaxor PORT MAP (c1, cin, s1 );
U2: compuertand2 PORT MAP (a, b, c2);
U3: compuertaor2 PORT MAP (a, b, c3);
U4: compuertand2 PORT MAP (c3, cin, c4 );
U5: compuertaor2 PORT MAP (c2, c4, cout);
end Behavioral;


.png)
.png)
Comentarios
Publicar un comentario